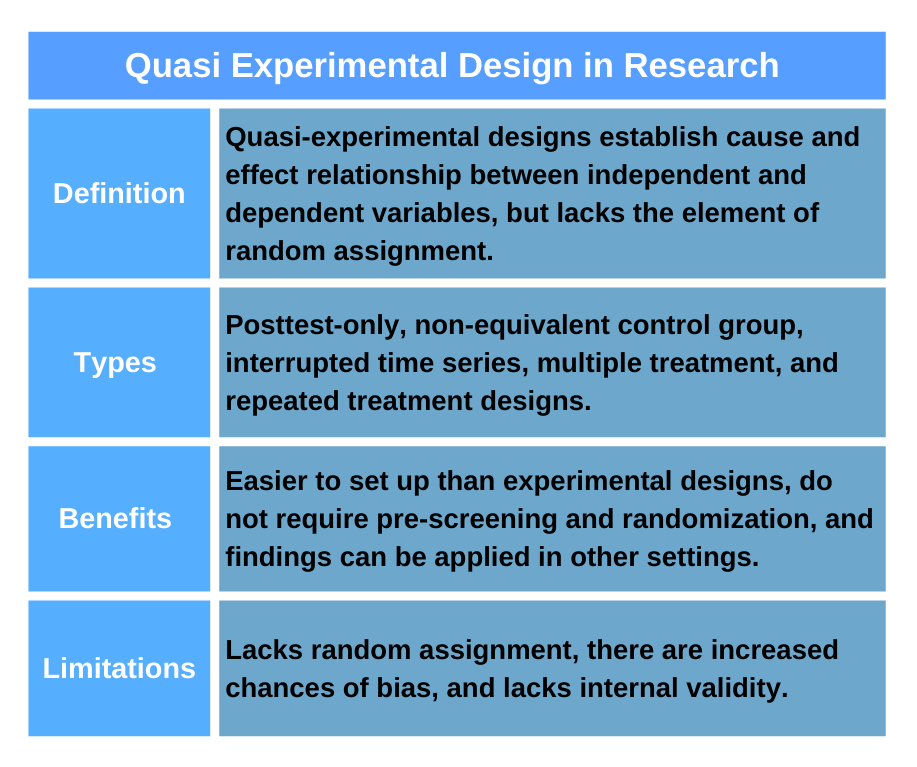
A quasi-experimental design is a research method that uses a non-experimental variation in the main independent variable of interest, emulating experimental conditions in which some subjects are exposed to treatment, and others are not on a random basis. Quasi experimental design involves the manipulation of the independent variable without the randomized assignment of participants to conditions. If you are in search of expert guidance on the quasi-experimental design in research, our professionals determine the cause-and-effect relationship of variables using criteria rather than randomization. This post is a comprehensive guide to the quasi-experimental design, highlighting its characteristics, types, benefits, when to use, and examples for reference.
What is a Quasi-Experimental Design in Research?
The quasi-experimental design is a research method that lacks the element of random assignment. It involves setting up an experiment where the researcher has little to no control over the factors being studied. Below are key characteristics of quasi-experimental design:- The main characteristic of quasi-experimental design is novelty. Novelty is the contribution of new information to an existing field of research.
- This design involves the use of designs like interrupted time series design and multiple time series design.
- Another characteristic is originality. The researcher uses innovative procedures to come up with original results crucial for decision-making.